By 2025, people will generate more than 181 zettabytes of data. To put it into perspective, the number is 181, followed by 21 zeros.
Yes, you read that right. We are living in a world where 5.07 billion people use the internet and a gigantic amount of data is being collected and stored every second.
If you run a business, you have to leverage the power of data and maximize its utilization. Every business, big or small, deals with a substantial amount of data on an everyday basis. They might have tools like MS Excel to help them sort through the data and come to a conclusion based on it. But what to do when this data is too large to deal with? That’s when you have to think of Big Data solutions.
As of now, 4 out of 10 companies use Big Data Cloud, and the majority of large and small businesses are focusing on Big Data tech implementation. To stay ahead of competitors, embrace innovations, and unlock incredible scalability potential, you must consider Big Data technology.
What is Big Data Cloud?
Big Data Cloud” refers to the combination of two major technological trends: Big Data and Cloud Computing. It is essentially the use of cloud-based resources to store, process, analyze, and manage large volumes of data. This is particularly valuable because it allows organizations to scale their computational resources up or down as needed, rather than investing in and managing physical hardware.
But before we proceed with the intricacy of Big Data Cloud let’s understand the fundamentals of Big Data and its far-reaching impact on businesses.

What are the types of big data?
Structured Data
Structured data is well-organized, quantitative in nature, and resides in a tabular or structured schema. In this type of data, you can access each discrete field separately or jointly with other data fields, depending on your requirements. Structured data is easy to analyze and allows organizations to collect data from multiple locations within a very short time. During the ETL process, structured data gets stored in a data warehouse.
Some examples of structured data are SKU numbers and pricing data in e-commerce, credit card numbers, patient data in hospitals, transactional details in banks, source and lead acquisition data in CRMs, and flight information and passenger data in the travel industry.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is devoid of any predefined conceptual definition, which makes it difficult to read. It cannot be easily processed or analyzed by traditional data models. While working with unstructured data, you have to train the application to interpret the information it is extracting. During the ETL process, unstructured data gets stored in a data lake.
For instance, rich media (including social media, podcasts, weather forecasts, entertainment, etc.), documents (email, web history, invoices), and IoT (data related to sensors and tickers) are examples of unstructured data.
Read More: How an Insurance Company Reduced Claimed Processing Time by 37% with Kanerika’s Data Solutions
Semi-structured Data
It is a combination of both structured and unstructured data types. It contains a few characteristics of structured data, but at the same time, it doesn’t come with a definite conceptual structure. To explain in simple words, semi-structured data is unstructured data with some metadata attached.
Let’s take an email for example. The email address of the sender and recipient, time, and IP address of the sender’s device are structured data, whereas the content of the email is unstructured data.

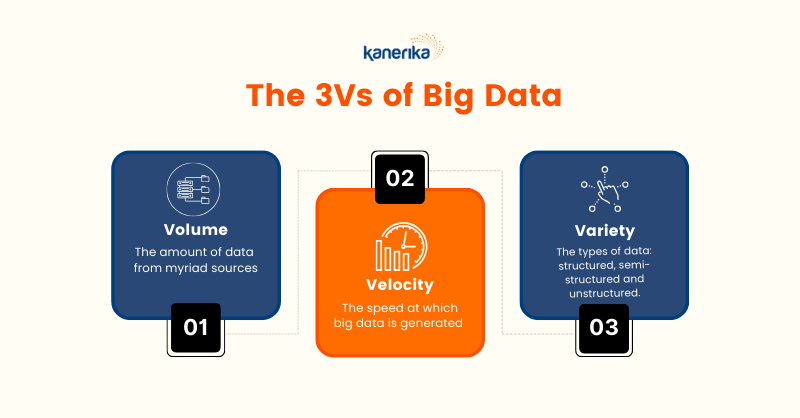
What are the three Vs of Big Data?
We can define big data using three Vs:
 3 Vs of Big Data
3 Vs of Big Data
Volume
Volume refers to the amount of data that organizations manage, analyze, and work with. When this data is massive, it is called big data. E.g: Instagram has a user base of 1.35 billion as of 2023, requiring a giant data warehouse to store and process the data.
Velocity
Velocity refers to the speed at which organizations generate, receive, accumulate, and process data. As technology continues to evolve and becomes more advanced, this speed goes up. E.g: Google processes around 99,000 search queries every second.
Variety
Refers to the diverse types of data that organizations receive, store, and manage, including structured data, unstructured data, and semi-structured data. E.g. e-commerce businesses deal with structured data like pricing data and SKU numbers and also perform sentiment analysis to review a product, which is unstructured data.

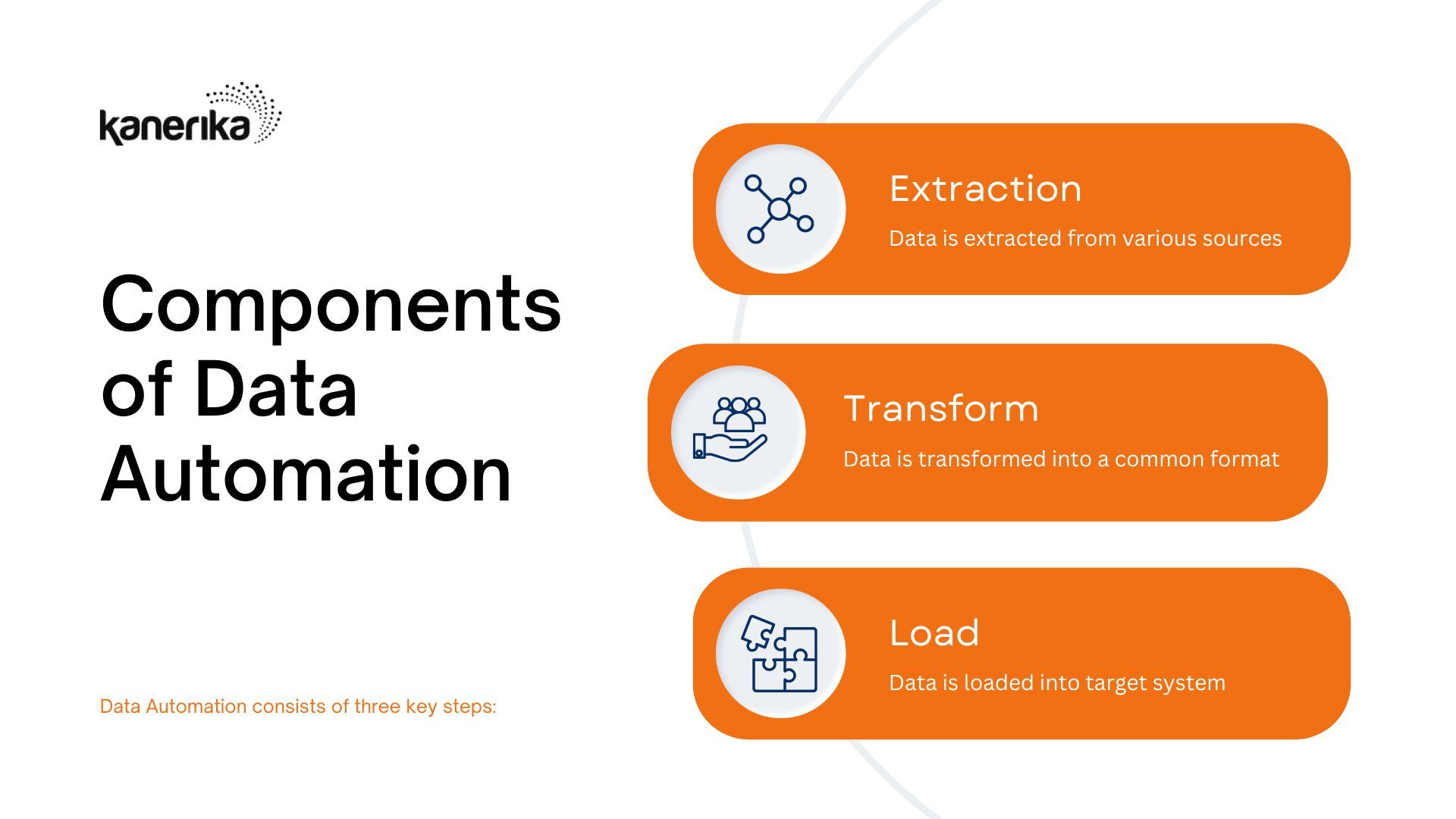
How Big Data Cloud Works?
Big Data Cloud works by leveraging the capabilities of cloud computing to store, process, and analyze large volumes of data. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Data Collection and Ingestion
Data is collected from various sources, which can include sensors, social media, transaction logs, mobile devices, and more. This data is then ingested into the cloud environment. Cloud platforms provide services for data ingestion, allowing for efficient and reliable transfer of data.
Data Storage
The ingested data is stored in cloud-based storage systems. Cloud providers offer various storage options, including object storage, file storage, and databases.
Data is typically stored in distributed and redundant fashion to ensure high availability and durability.
Read More: What is Data Warehouse?
Data Processing
Big Data processing frameworks and tools are used to handle large volumes of data. This can include technologies like Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and others. These frameworks distribute the processing tasks across multiple nodes in a cluster, allowing for parallel processing and efficient handling of large datasets.
Scaling
One of the key advantages of Big Data Cloud is scalability. When the volume of data increases, or when more processing power is needed, cloud resources can be scaled up. This can be done by adding more virtual machines or utilizing higher-tier services.
Analysis and Analytics
Once the data is processed, it can be subjected to various types of analysis. This can include descriptive analytics (summarizing data), diagnostic analytics (identifying patterns and trends), predictive analytics (forecasting future trends), and prescriptive analytics (suggesting actions to take).

Machine Learning and AI
Big Data Cloud environments often support machine learning and AI capabilities. This allows organizations to build and train models on large datasets to make predictions, classify data, and automate decision-making processes.
Data Visualization and Reporting
The results of the analysis can be visualized through dashboards, reports, and other visualization tools. These provide a clear and understandable representation of the insights gained from the data.
Read More: The Role of Data Visualisation in Business Analytics – Is it worth the investment?
Data Security and Compliance
Cloud providers implement robust security measures to protect data. This includes encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Data Lifecycle Management
Cloud platforms offer tools and services for managing the lifecycle of data. This includes data retention policies, archiving, and deletion of data as needed to optimize storage costs.
Data Integration
Big Data Cloud environments often integrate with other systems and services, allowing for seamless data flows between different applications and platforms.
By combining the power of cloud computing with Big Data technologies, organizations can efficiently process and analyze large volumes of data, extract meaningful insights, and make data-driven decisions. This approach provides flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in handling Big Data workloads.

Advantages Of Big Data Processing
Big Data can help modern businesses in more ways than one. In this section, we’ll delve into the benefits of Big Data processing.
Informed decision making
Businesses can derive valuable insights with the help of big data, allowing leaders to make data-driven business decisions across various departments. These decisions pave the way for businesses and organizations to focus on quality, without compromising on scalability.
Here are some examples:
- E-commerce stores can design more effective target campaigns using Big Data
- HR departments can implement Big Data processing to improve their recruitment processes
- Big Data provides a better understanding of market trends and consumer sentiments, which helps in product development
- Educational institutions can implement Big Data to track students’ performance, identify problem areas, and tailor their teaching methods to improve learning outcomes
Improved productivity
Big Data can make the life of IT specialists simpler. With Big Data implementation, they won’t have to manually sort through all types of data—the process will be automated, helping employees save time and redirect their focus on tasks that require human involvement.
As Big Data helps companies analyze large chunks of data within a very short time, it increases productivity across departments and speeds up business processes.
Read More: How an IT Firm Achieved a Week’s Work in Just Hours with AI-Powered Marketing Automation
Improved customer service
Customers are the lifeblood of any business, so improving customer service should always be a priority.
Here’s how Big Data helps refine the customer experience at various levels:
- Collecting and analyzing vast amounts of customer information (e.g.: browsing behavior, purchase history, feedback, etc.) provides insight into customer preferences and emerging trends
- Companies can tailor their customer interactions and product recommendations based on the derived insights
- Businesses can resolve customers’ issues quickly with real-time analysis
- Companies can track employee performance and customer satisfaction metrics to improve their service

Reduced costs
Big data helps cut down costs by optimizing different aspects of a business. It promotes efficiency in business processes, mitigates risks, and ensures companies don’t have to spend on unnecessary or unpredictable expenses.
Here are some examples:
- In-depth data analysis helps in identifying inefficiencies at an early stage
- Big data helps in optimizing energy consumption and resource utilization, reduces utility bills, and helps businesses become more environmentally friendly
- Big data comes in handy for fraud detection and prevention, saving companies money by detecting irregularities in financial transactions.
- Data-driven predictive maintenance increases the shelf life of machinery, thus cutting down the expenses of frequent replacements.

What are the Challenges of Big Data?
While Big Data can be a savior for companies, it does come with a few challenges.
Compliance issues
Businesses that store, process, and utilize the personal information of customers have to meet rigorous federal and industry regulation standards (GDPR in the European Union, for example). This is why it’s important to have a compliance officer at your company, who will help navigate through any compliance issues that might emerge.
Cybersecurity threats
At a time when the volume and complexity of data continue to be more and more intense, companies using Big Data solutions are at high risk of cyberattacks. Businesses have to be vigilant of cyber criminals and take actions to mitigate these risks, such as training employees about the importance of cybersecurity and implementing cybersecurity solutions that can detect and eliminate threats before they become a problem.
Kanerika offers top-notch ML driven RPA solutions that help in fraud detection, customer service, risk assessment & mitigation, fraud prevention, substantial operational excellence, suspicious behavior detection, and regulatory compliance. Kanerika deploys long-term intelligent automation strategy and AI fraud detection models that will bring exceptional results.
To know more about the services, click here.
Finding the right talent
Working with Big Data often requires a high level of technical expertise. 77% of businesses report that they are finding it difficult to fill vacant roles, which can lead to a massive talent gap. Unless you have a stellar team of data scientists and experts on board, you may not be able to make the most of Big Data implementation.

Big Data Cloud Use Cases
The use case of Big Data goes wide and far. From digital companies to brick-and-mortar establishments, every type of business can use Big Data to have a competitive edge in their respective industry.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, you can implement Big Data for predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, defect detection and quality control.
For instance, for predictive maintenance, data from sensors on the machinery is collected in real-time and stored in the cloud. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to predict maintenance needs. Similarly, cloud-based analytics platforms process data from various sources, including suppliers, transportation providers, and production facilities that allows for real-time tracking and optimization of the supply chain.
Also Read: How Kanerika’s Cloud Based Solutions Empowered Global Consumer Goods Company in the USA optimize their Supply Chain
Healthcare
From remote patient care to drug discovery and population management health – big data solutions can open up a new world to the healthcare industry. It can help in genomic research by identifying particular disease genes and biomarkers, improve patient experience, and find areas where cash flows can be improved.
Wearable devices, electronic health records and other cloud-based platforms can store and process critical data that can identify trends, assess treatment effectiveness, identify potential candidates for trials as well prevent sudden deaths. The impact of Big Data Cloud in healthcare is indeed profound and far-reaching!
Retail
Retail companies can embrace innovation with Big Data Cloud services and thrive in this competitive industry. Big data helps in developing marketing strategies and campaigns based on customer preferences, personalizing customer experience, identifying high-value customers to create targeted campaigns for, and identifying price movement opportunities.

Additionally, surveillance cameras and point-of-sale systems generate data, which is sent to the cloud for analysis. Machine learning algorithms can detect suspicious patterns, helping to prevent theft and fraud.
Besides the ones mentioned above, Big Data Cloud solutions can be implemented in a wider range of industries, including education, transportation, oil and gas, government organizations, insurance, media and communications, banking, agriculture, and real estate, to mention a few.
Wrapping Up
Big data has been and continues to be a transformative force that not only helps businesses tap into the latent potential of data but also opens up new opportunities for them to evolve and be future-ready.
When you implement it properly, you will experience smooth operational efficiency, increased productivity, and your business decisions will be more precise and data-driven than ever, propelling monumental growth.
To achieve such an outcome, businesses must partner with technology experts who not only comprehends the intricacies of Big Data but also demonstrates the adeptness to execute it flawlessly. Enter Kanerika, a foremost data cloud service provider boasting a combined wealth of 75 years of experience.
With a proven track record in harnessing the power of Big Data Cloud, Kanerika empowers businesses to stay competitive and ahead of the curve, ensuring that your organization not only adopts Big Data solutions but also leverages them to their full potential.
Our tailored approach to data management and cloud solutions is designed to align seamlessly with your business objectives. From strategic planning to implementation and ongoing support, their expertise covers the full spectrum of Big Data Cloud services. This holistic approach guarantees that your business remains future-ready, equipped to adapt to evolving trends and challenges.
Partnering with Kanerika means more than just adopting Big Data Cloud; it means unlocking the true power of data for your business. With our guidance and expertise, you can confidently navigate the complexities of data management, driving operational efficiency, boosting productivity, and making decisions that are not just informed, but precise and data-driven.
If data is the lifeblood of your enterprises, Kanerika will be your trusted ally, dedicated to helping you thrive in the age of Big Data Cloud.

FAQs
How Does Big Data Cloud Impact the Healthcare Industry?
Big Data Cloud significantly impacts healthcare by enabling genomic research, improving patient experiences, and optimizing financial management. It can analyze data from wearable devices and electronic health records to provide critical healthcare insights.
How Can Retail Companies Benefit from Big Data Cloud?
Retail companies can use Big Data Cloud to analyze customer behavior, personalize shopping experiences, identify valuable customers, and optimize pricing strategies, thus staying competitive in the market.
How can organizations ensure data security when using Big Data Cloud solutions?
Cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, data lifecycle management and integration with cybersecurity solutions help protect sensitive data.
What are the three Vs of Big Data, and why are they important?
The three Vs of Big Data are Volume, Velocity, and Variety. Volume refers to the amount of data, Velocity is the speed at which data is generated, and Variety represents the different types of data. These factors are important because they define the challenges and opportunities associated with Big Data processing.
What role does machine learning and AI play in Big Data Cloud environments?
Big Data Cloud environments often support machine learning and AI capabilities. This enables organizations to build and train models on large datasets for tasks such as predictions, data classification, and automated decision-making processes.
How can businesses find the right technology partner to implement Big Data Cloud solutions?
Businesses seeking to implement Big Data Cloud solutions should look for technology experts with experience in the field. Partnering with providers like Kanerika, who have a track record in harnessing the power of Big Data Cloud, can ensure successful implementation aligned with business objectives.
What are the examples of real-world use cases of Big Data Cloud across different industries?
Big Data Cloud is transforming various industries. In manufacturing, it's used for predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization. Healthcare leverages it for genomic research and patient experience enhancement. Retail benefits from customer-centric marketing and price analysis. Entertainment utilizes it for personalized content recommendations and fraud detection. Education tracks student performance and tailors teaching methods. Finance relies on it for fraud prevention and operational excellence. These real-world use cases demonstrate the wide-reaching impact of Big Data Cloud across diverse sectors.
In what ways does Big Data help in enhancing customer service and customer experience?
It enables businesses to analyze vast amounts of data to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. With real-time analysis, companies can respond swiftly to customer needs and resolve issues promptly. Personalized recommendations and interactions based on data-driven insights improve customer satisfaction.
What are the key benefits of adopting Big Data Cloud solutions for businesses?
It enables cost-effective scalability, allowing organizations to handle large data volumes efficiently. Enhanced data processing and analytics capabilities lead to informed decision-making, boosting productivity and quality. Improved customer service through data-driven insights enhances customer satisfaction.
What are the potential benefits of implementing Big Data Cloud solutions for businesses?
Implementing Big Data Cloud solutions can lead to increased operational efficiency, improved productivity, more precise data-driven decision-making, and overall business growth. It empowers organizations to tap into the potential of data and stay competitive.