Did you know that 89% of enterprises now have a multi-cloud strategy? According to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud Report, organizations are increasingly turning to multi-cloud solutions to meet their diverse computing needs. This has now become a fundamental change in how businesses approach their IT infrastructure. Multi-cloud migration is a critical strategy for companies looking to enhance flexibility, reduce costs, and mitigate risks in an ever-evolving digital environment.
But what exactly is multi-cloud migration, and why has it become so crucial for businesses of all sizes? Regardless of whether you’re running a startup or a large corporation, understanding the intricacies of multi-cloud migration can be the key to staying competitive in today’s fast-paced tech world. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the benefits, challenges, and strategies of multi-cloud migration, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate this complex but rewarding process.
What is Multi-cloud Migration?
The process of multi-cloud migration involves transferring an organization’s assets, applications, and infrastructure from on-premises environments or a single cloud provider to multiple cloud platforms. In this regard, it entails splitting up workloads across different cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
For instance, a retail company may decide to migrate its e-commerce platform to AWS because of its ability to scale, use Azure for data analytics due to its sophisticated AI capabilities, and take advantage of GCP, which provides container orchestration services. These steps help optimize operational cost and performance while mitigating vendor lock-in. The whole process requires a well-thought-out plan, application audit, data movement activity, and network restructuring for uninterrupted operations across many cloud environments.

Reasons for Adopting a Multi-cloud Strategy
1. Risk Mitigation
Multi-cloud migration significantly enhances an organization’s ability to mitigate risks associated with cloud computing. By distributing workloads across multiple providers, companies reduce their vulnerability to single points of failure. This strategy ensures that if one cloud service experiences issues, others can maintain operations, minimizing downtime and potential data loss. Additionally, multi-cloud setups offer improved disaster recovery options and strengthen overall business continuity plans.
Key Points
- Reduces dependency on a single provider
- Improves disaster recovery capabilities
- Enhances business continuity
- Minimizes vulnerability to service outages
2. Cost Optimization
Adopting a multi-cloud approach opens up new avenues for cost optimization. Organizations can leverage the competitive pricing landscape of cloud services, selecting the most cost-effective solutions for different workloads. This flexibility allows companies to avoid overpaying for resources they don’t need while ensuring they have access to high-performance options when required. Moreover, multi-cloud strategies enable businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, further optimizing costs.
Key Points
- Allows leveraging of competitive pricing across providers
- Enables matching workloads to cost-effective solutions
- Provides flexibility to scale resources as needed
- Reduces overall IT infrastructure costs
3. Performance Enhancement
Multi-cloud migration can lead to significant improvements in application and service performance. By choosing the best-fit services from different providers, organizations can optimize their applications for speed, reliability, and efficiency. This approach allows companies to reduce latency by selecting geographically closer data centers for specific regions. Furthermore, multi-cloud setups enable effective load balancing across providers, ensuring consistent performance even during peak usage periods.
Key Points
- Improves application performance by using best-fit services
- Reduces latency by choosing geographically closer data centers
- Enables load balancing across multiple providers
- Optimizes overall system efficiency

4. Avoiding Vendor Lock-in
One of the most compelling reasons for multi-cloud migration is the avoidance of vendor lock-in. By diversifying cloud providers, organizations maintain greater control over their IT infrastructure and data. This strategy facilitates easier migration between providers if needed, giving companies more flexibility in their technology choices. It also strengthens an organization’s negotiating position with cloud vendors, as the ability to easily switch providers can lead to better terms and pricing.
Key Points
- Prevents over-reliance on a single cloud ecosystem
- Facilitates easier migration between providers if needed
- Maintains negotiating power with cloud vendors
- Increases flexibility in technology choices
5. Improved Resilience and Redundancy
Multi-cloud migration significantly enhances an organization’s resilience and redundancy capabilities. By distributing workloads and data across multiple cloud providers, companies create a more robust infrastructure that can withstand various types of failures or disruptions. This approach ensures that if one cloud service experiences issues, others can seamlessly take over, maintaining continuous operations. Additionally, multi-cloud setups allow for more sophisticated backup and disaster recovery strategies, further strengthening an organization’s ability to bounce back from potential setbacks.
Key Points
- Distributes risk across multiple cloud providers
- Ensures continuity of operations during provider-specific outages
- Enables more robust backup and disaster recovery strategies
- Reduces the impact of localized failures or cyber attacks
6. Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
Multi-cloud migration offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability for organizations. This approach allows businesses to choose the most suitable services from different providers based on specific workload requirements, performance needs, or cost considerations. Companies can easily scale their resources up or down across various cloud platforms to meet changing demands. This flexibility extends to geographical expansion as well, enabling organizations to quickly deploy services in new regions by leveraging the global infrastructure of multiple cloud providers.
Key Points
- Allows selection of best services for specific workloads
- Enables rapid scaling of resources across multiple platforms
- Facilitates easy expansion into new geographical markets
- Provides agility to adapt to changing business needs
7. Compliance with Data Sovereignty Requirements
In an era of increasing data regulation, multi-cloud migration offers a powerful solution for meeting complex data sovereignty requirements. Organizations can strategically place data in specific geographical locations to comply with regional data protection laws and regulations. This approach allows companies to maintain local copies of data where required, while still leveraging global cloud infrastructure for processing and analytics. Multi-cloud strategies also provide the flexibility to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes, ensuring ongoing compliance.
Key Points

Planning Your Multi-cloud Migration Strategy
1. Assessing Current Infrastructure and Applications
The first step in planning a multi-cloud migration strategy involves a comprehensive assessment of your existing IT landscape. This process requires a detailed inventory of all applications, data, and infrastructure components. By understanding the current state of your IT environment, you can identify which workloads are suitable for migration, which may need refactoring, and which should remain on-premises. This assessment also helps in determining interdependencies between applications and data, crucial for planning a smooth migration.
- Conduct a thorough inventory of applications and infrastructure
- Identify workloads suitable for cloud migration
- Determine application and data interdependencies
- Assess the need for application refactoring or modernization
2. Defining Migration Goals and Objectives
Clearly defining your migration goals and objectives is crucial for the success of your multi-cloud strategy. This step involves aligning your cloud migration plans with broader business objectives and identifying specific outcomes you want to achieve. Whether it’s cost reduction, improved scalability, enhanced performance, or better compliance, having well-defined goals helps in making informed decisions throughout the migration process. It also provides a framework for measuring the success of your migration efforts.
- Align cloud migration with business objectives
- Set specific, measurable goals for the migration
- Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) for success
- Establish timelines and milestones for the migration process
3. Selecting the Right Cloud Providers
Choosing the right mix of cloud providers is a critical aspect of multi-cloud migration. This process involves evaluating various factors to ensure the selected providers can meet your specific needs. Start by assessing the service offerings of different providers, comparing their pricing models, and evaluating their geographical presence. Consider factors such as performance, security features, compliance certifications, and support services. It’s also important to assess the provider’s long-term viability and roadmap to ensure they align with your future needs.
- Evaluate service offerings of different cloud providers
- Compare pricing models and total cost of ownership
- Assess geographical presence and data center locations
- Consider provider’s security features, compliance certifications, and support services
4. Creating a Detailed Migration Roadmap
Developing a comprehensive migration roadmap is essential for a successful multi-cloud transition. This roadmap should outline the step-by-step process for migrating each application or workload to the chosen cloud environments. It should include timelines, resource allocation, and potential risks and mitigation strategies. The roadmap should also account for testing and validation phases, as well as plans for business continuity during the migration process. Regular review and adjustment of the roadmap ensure it remains aligned with your goals and adapts to any challenges encountered.
- Develop a phased approach for migrating applications and data
- Allocate resources and set realistic timelines for each phase
- Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies
- Include testing and validation phases in the roadmap
5. Establishing Governance and Compliance Frameworks
Implementing robust governance and compliance frameworks is crucial for managing a multi-cloud environment effectively. This involves developing policies and procedures for cloud resource management, security, and compliance across all cloud platforms. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for managing the multi-cloud environment and implement tools for monitoring and reporting across all cloud services. Additionally, ensure that your governance framework addresses data privacy regulations and industry-specific compliance requirements across all cloud environments.
- Develop comprehensive policies for cloud resource management
- Implement security and compliance procedures across all cloud platforms
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for multi-cloud management
- Implement tools for monitoring, reporting, and ensuring compliance across cloud services

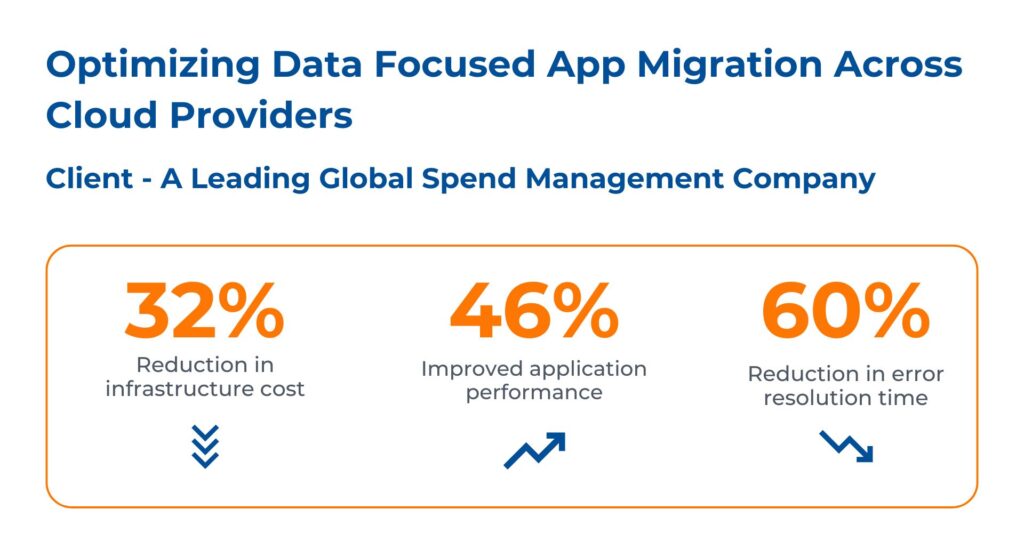
Case Study: Optimizing Data Focused App Migration Across Cloud Providers
Business Challenges
The client is a prominent Spend Management Company that wanted to ensure a smooth migration to their newly developed cloud-native platform, without disrupting the customer experience.
Kanerika’s Solutions
By leveraging Informatica and Kafka technologies, Kanerika has offered the following solutions to address the client’s problems:
Key Steps in the Multi-cloud Migration Process
1. Application Assessment and Categorization
Application assessment and categorization is a crucial first step in the multi-cloud migration process. This phase involves a detailed analysis of your application portfolio to determine the best migration strategy for each application.
Applications are typically categorized into three groups:
Cloud-ready Applications: These are modern applications that can be easily moved to the cloud with minimal modifications. They often use microservices architecture and are containerized, making them highly portable.
Applications Requiring Modernization: These applications may need some refactoring or re-architecting to fully leverage cloud capabilities. This could involve breaking monolithic applications into microservices or optimizing them for cloud-native features.
Legacy Applications: These are older applications that may not be compatible with cloud environments without significant modifications. In some cases, it might be more cost-effective to replace these with cloud-native alternatives.
Key Actions
- Conduct a thorough inventory of all applications
- Assess each application’s cloud readiness
- Identify dependencies and integration requirements
- Determine the appropriate migration strategy for each application
2. Data Migration Planning
Data migration planning is a critical step that involves carefully mapping out how data will be moved to the cloud. This process begins with data classification and prioritization, where data is categorized based on its sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and business importance.
Once data is classified, appropriate data transfer methods need to be chosen. These could range from online transfer for smaller datasets to physical transfer methods like AWS Snowball for large volumes of data. The choice depends on factors such as data volume, available bandwidth, and time constraints.
Key Actions
- Classify data based on sensitivity and regulatory requirements
- Prioritize data for migration based on business importance
- Choose appropriate data transfer methods
- Plan for data validation and integrity checks post-migration

3. Network Architecture Design
Designing the network architecture for a multi-cloud environment is crucial for ensuring seamless communication between different cloud platforms and on-premises systems. This involves creating a network topology that allows for secure and efficient data transfer between clouds.
Implementing software-defined networking (SDN) is often a key part of this process. SDN provides the flexibility and programmability needed to manage complex multi-cloud networks effectively. It allows for dynamic routing, load balancing, and security policy enforcement across multiple cloud environments.
Key Actions
- Design network topology for multi-cloud connectivity
- Implement software-defined networking for flexibility
- Ensure secure and efficient inter-cloud communication
- Plan for scalability and future growth in network design
4. Security and Identity Management
Security is paramount in a multi-cloud environment. Implementing robust multi-cloud security solutions is essential to protect data and applications across all cloud platforms. This involves deploying security tools that can provide consistent protection across diverse cloud environments.
Managing identities across cloud environments is another crucial aspect. This typically involves implementing a centralized identity and access management (IAM) solution that works across all cloud platforms. Single sign-on (SSO) capabilities are often implemented to simplify user access while maintaining security.
Key Actions
- Implement comprehensive multi-cloud security solutions
- Deploy centralized identity and access management
- Enable single sign-on across cloud platforms
- Ensure consistent security policies across all environments
5. Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Setting up multi-cloud monitoring tools is essential for maintaining visibility across all cloud environments. These tools should provide a unified view of performance metrics, resource utilization, and costs across all cloud platforms.
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and service level agreements (SLAs) is crucial for measuring the success of your multi-cloud strategy. KPIs might include metrics like application response times, resource utilization efficiency, and cost savings. SLAs define the expected performance levels for various services and applications.
Continuous optimization is key in a multi-cloud environment. This involves regularly reviewing performance data, identifying inefficiencies, and making adjustments to improve performance and reduce costs.
Key Actions
- Implement multi-cloud monitoring tools for comprehensive visibility
- Define relevant KPIs for measuring cloud performance and efficiency
- Establish clear SLAs for all cloud services
- Regularly review and optimize cloud resource usage and performance

What Are the Tools and Technologies Required for Multi Cloud Migration?
1. Cloud Management Platforms
The most important aspect of multi-cloud migration is the cloud management platforms, which offer a combined resource for managing each resource across multiple cloud providers. These platforms can provision resources, manage costs, and monitor performance.
Some popular options include IBM Cloud Pak for Multi-cloud Management, Morpheus, and VMware vRealize Suite. These tools simplify multi-cloud environment complexities, enabling organizations to sustain uniformity and control in different clouds.
2. Container Orchestration Tools
These are now essential in multi-cloud approaches, with Kubernetes leading the way. It provides businesses with a standardized way of deploying, operating, and scaling containerized applications within various cloud environments, thus giving them portability and consistency.
Other alternatives in this field comprise Docker Swarm and Apache Mesos, but nonetheless, Kubernetes has become the prevailing standard by which all container orchestration methods are measured in multi-cloud configurations.
3. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Tools
IaC tools have transformed how cloud resources are allocated and supervised today. Some examples include Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible. These tools allow organizations to comprehend their infrastructure using code while maintaining similarity and repeatability across diverse cloud environments.
IaC acts as an infrastructural version control system that mitigates human errors while empowering developers to quickly deploy codes into running systems. These tools will be very useful when you want to ensure consistency among different cloud platforms, particularly during complex deployment processes.
4. Multi-cloud Security Solutions
These help protect data, including other information hosted on distinct clouds, from destruction. They combine several security functions, such as identity and access management, encryption, threat detection, compliance monitoring, etc.
For example, Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Network, Aqua Security, and Check Point CloudGuard offer comprehensive security solutions for multiple clouds. This enables organizations to maintain consistent security, patch vulnerabilities alone, and keep up with each cloud’s regulatory requirements.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are increasingly being leveraged for cloud optimization in multi-cloud environments. The technology can analyze large volumes of data across various clouds to determine how well resources are used and whether there is room for cost efficiencies or even performance improvements.
AI-based tools predict resource needs, automate scaling decisions, and identify possible issues before they affect performance. IBM Watson AIOps or Google’s Anthos provide optimized multi-cloud operations driven by AI/ML, including anomaly detection, predictive analytics, automated problem resolution, etc.

Best Practices for Successful Multi-cloud Migration

1. Pilot Project
Starting with a pilot project is a crucial first step in multi-cloud migration. This approach allows organizations to test their migration strategy on a smaller scale before committing to a full-scale transition. A pilot project helps in:
- Identifying potential challenges and bottlenecks
- Validating the chosen tools and technologies
- Gaining valuable insights for the broader migration
- Building confidence among stakeholders
2. Phased Approach
Implementing a phased approach is essential for managing the complexity of multi-cloud migration. This strategy involves breaking down the migration process into manageable stages, typically starting with non-critical applications and gradually moving to more critical systems. A phased approach offers several benefits:
- Reduces risk by allowing for adjustments based on lessons learned
- Minimizes disruption to business operations
- Allows for better resource allocation and management
- Provides opportunities for continuous improvement throughout the migration process
3. Automation
Prioritizing automation is key to achieving efficiency and consistency in multi-cloud environments. Automation tools can streamline various aspects of the migration process and ongoing management:
- Infrastructure provisioning and configuration
- Application deployment and updates
- Security policy enforcement
- Performance monitoring and optimization
4. Documentation
Ensuring proper documentation is critical for maintaining clarity and continuity throughout the migration process and beyond. Comprehensive documentation should cover:
- Migration strategies for each application and dataset
- Network architecture and security configurations
- Operational procedures and troubleshooting guides
- Compliance and governance policies
This documentation serves as a valuable resource for current and future team members, ensuring consistency in management practices and facilitating knowledge transfer.
5. Employee Training
Investing in employee training and skill development is crucial for the long-term success of a multi-cloud strategy. As multi-cloud environments require a diverse set of skills, organizations should:
- Provide training on various cloud platforms and technologies
- Encourage certifications in relevant cloud and DevOps skills
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation
- Consider hiring specialists or partnering with expert consultants
6. Evaluation
Regular review and optimization of cloud usage is essential for maintaining an efficient and cost-effective multi-cloud environment. This ongoing process involves:
- Monitoring resource utilization across all cloud platforms
- Identifying and eliminating unused or underutilized resources
- Optimizing workload placement based on performance and cost metrics
- Staying updated with new cloud features and pricing models to leverage cost-saving opportunities

Challenges in Multi-cloud Migration
1. Complexity in Management and Orchestration
It is difficult to manage several cloud environments without controlling different platforms, each with its unique set of tools, APIs, and management interfaces. This means that IT departments need to ensure that they run seamlessly across these providers, increasing their overhead. Sophisticated means of doing this involve workloads distribution, resource allocation, and monitoring. Poorly managed business processes cause inefficiencies and increased operational challenges.
2. Security and Compliance Concerns
Maintaining uniformity in security policies and compliance with multiple cloud environments is difficult. If not properly managed, each provider has diverse security measures, leading to gaps in protection. Moreover, this migration could become complex when it comes to adherence to various regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) across different jurisdictions. To reduce these risks, businesses should constantly implement comprehensive security strategies and monitor compliance.
3. Data Integration and Interoperability Issues
The challenge of integrating data across disparate cloud platforms arises from differences in data formats, APIs, and services provided by distinct vendors within cloud computing. This may lead to data silos where information is locked within a single cloud environment, making it impossible for one person or team to have a holistic view of the facts it holds. Ensuring interoperability requires robust data integration solutions and strategies to harmonize data flows and maintain consistency across platforms.
4. Skills Gap and Training Requirements
Specialized skills for managing multi-cloud environments are needed for effective management and operation. Organizations usually face a situation where their IT personnel do not have enough expertise to operate all the hardware deployed on different clouds simultaneously, requiring extensive training or employing new staff who specialize in these areas. Continuous learning is required for employees to keep up with each cloud provider’s new features and best practices every other day.
5. Cost Management Across Multiple Providers
The complexity of billing and the different providers’ patterns of use make cost management difficult in a multi-cloud setup. Budget overruns can happen if organizations don’t have proper cost management strategies in place. Cost monitoring, analysis, and optimization tools and techniques are essential for efficiently using cloud resources. This requires using cost management tools, creating budgets, and continuously optimizing resource utilization that is aligned with business objectives.

Real-life Examples of Multi-cloud Migration
1. Netflix
Netflix is a prime example of successful multi-cloud migration and usage. While primarily using Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its streaming services, Netflix has also incorporated Google Cloud Platform (GCP) into its infrastructure.
Use Cases
- AWS for content delivery and streaming.
- GCP for disaster recovery and big data analytics
Benefits
- Enhanced global content delivery
- Improved disaster recovery capabilities
- Advanced analytics for content recommendations
Netflix’s multi-cloud approach has allowed it to maintain its position as a leading streaming service, ensuring high availability and performance for its global user base.
2. Spotify
Spotify, the popular music streaming platform, has embraced a multi-cloud strategy involving Google Cloud Platform and Amazon Web Services.
Use Cases
- GCP for data processing and machine learning
- AWS for specific services and geographical coverage
Benefits
This multi-cloud approach has enabled Spotify to deliver personalized music experiences to millions of users worldwide while optimizing costs and performance.
3. Airbnb
Airbnb, the online marketplace for lodging and tourism experiences, utilizes a multi-cloud strategy incorporating Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform.
Use Cases
- AWS for core infrastructure and services
- GCP for big data processing and machine learning
Benefits
Airbnb’s multi-cloud strategy has allowed it to leverage the strengths of different cloud providers, enhancing its ability to process vast amounts of data and provide personalized experiences to users.
4. HSBC
HSBC, one of the world’s largest banking and financial services organizations, has adopted a multi-cloud strategy using Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure.
Use Case
Distributed workloads across multiple cloud providers
Benefits
HSBC’s multi-cloud approach has enabled it to meet complex regulatory requirements in different countries while improving its ability to innovate and deploy new financial services.
5. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, the global beverage giant, has implemented a multi-cloud strategy utilizing Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services.
Use Case
Distributed application hosting and data analytics
Benefits
- Improved global presence and reduced latency
- Enhanced data analytics capabilities
- Increased flexibility in deploying marketing campaigns
Coca-Cola’s multi-cloud strategy has allowed it to optimize its global IT infrastructure, improve customer engagement through data-driven marketing, and enhance its ability to respond to market changes quickly.
Experience Seamless and Efficient Multi-cloud Migration with Kanerika’s Expertise
Businesses should partner with Kanerika for their multi-cloud migration needs due to our extensive expertise in cloud management services. At Kanerika, we specialize in cloud migration, transformation, and adoption, ensuring a smooth transition to a multi-cloud environment. Our use of advanced tools and technologies guarantees a safe and efficient migration, minimizing disruptions and optimizing performance.
Our comprehensive service portfolio extends beyond cloud solutions. We also offer cutting-edge AI/ML, data governance, data analytics, and RPA services, helping businesses leverage technology to gain a competitive edge. Our commitment to quality and security is validated by our ISO 27001 and 27701 certifications, along with our CMMI Level 3 certification, which underscores our dedication to delivering high-standard services.
Partnering with us means accessing a team of experts who understand the intricacies of multi-cloud environments and are equipped to handle the complexities involved. Our tailored solutions are designed to meet the unique needs of each business, ensuring enhanced resilience, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Choose Kanerika for a reliable, secure, and seamless multi-cloud migration experience.

Frequently Asked Questions
How would you define multi-cloud migration?
Multi-cloud migration involves moving data, applications, and services to multiple cloud environments, utilizing various providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This approach enhances resilience, flexibility, and cost-efficiency by distributing workloads across different platforms, reducing dependency on a single provider, and improving disaster recovery capabilities.
Can you provide an example of multi-cloud migration?
Airbnb is a prime example of multi-cloud migration. Initially relying on AWS, Airbnb integrated Google Cloud for data analytics and machine learning. This allowed Airbnb to leverage Google Cloud's robust data processing capabilities while maintaining AWS for computing needs, thus optimizing performance and scalability across different cloud platforms.
What benefits does multi-cloud migration offer?
Multi-cloud migration offers several advantages, including improved resilience through redundancy, enhanced flexibility and scalability, cost optimization by leveraging competitive pricing from different providers, increased security with diverse security measures, and compliance with data sovereignty requirements by choosing providers with specific regional capabilities.
Does Azure support multi-cloud environments?
Yes, Azure supports multi-cloud environments. Organizations can integrate Azure with other cloud providers like AWS and Google Cloud to create a multi-cloud strategy. This allows businesses to leverage Azure's strengths in specific areas while utilizing other providers for different services, thus enhancing overall flexibility and resilience.
What purposes does multi-cloud migration serve?
Multi-cloud migration serves various purposes, including improving disaster recovery, enhancing data redundancy, optimizing costs by leveraging multiple pricing models, ensuring compliance with regional data regulations, and increasing operational flexibility by using the best services from different cloud providers to meet specific business needs.
What different strategies exist for cloud migration?
The main cloud migration strategies are Rehosting (Lift and Shift), Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift), Refactoring (Re-architecting), Rebuilding, and Replacing. Each strategy varies in complexity and impact, allowing businesses to choose the best approach based on their specific needs and goals.