Business intelligence is one of the most preferred technology choices for enterprises of all sizes worldwide. The United States of America has the highest BI adoption rate globally, standing at 30.9%, and is also the largest revenue generator in the BI sector, with an estimated $13.15 billion in 2023.
BI is a strategic approach to transforming raw data into clear, concise information that empowers businesses to make smarter decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge. In this guide, we’ll delve into its core functionalities, explore its applications across various departments, and help you understand the steps involved to build a winning BI strategy.
What is Business Intelligence?
Organizations today generate massive amounts of data – customer transactions, marketing campaigns, production logs, financial records, and the list goes on. But data itself is just a collection of numbers and text. The true magic lies in extracting valuable insights from this data, and that’s where BI comes in.
Business intelligence (BI) can be understood as a combination of strategies, technologies, and practices that organizations use to analyze their data and gain valuable insights. It’s essentially all about turning raw data into actionable information that can inform better decision-making across all levels of a business.

How Business Intelligence Works: Understanding the 5 Core Components
Business Data Intelligence works by combining these components into a streamlined process.
1. Data Collection
This process involves gathering raw data from various sources both within and outside the organization. Internal data sources include transactional databases, CRM systems, and operational metrics, while external data can come from market research, social media, and third-party data vendors.
Internal Sources:
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems: Track customer interactions, sales history, and purchase behavior
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems: Manage financial data, inventory levels, and production processes
- Marketing automation platforms: Provide data on campaign performance, website traffic, and customer engagement
- Human Resource Management (HRM) systems: Store employee information, performance data, and training records
External Sources:
- Market research reports: Offer insights on industry trends, customer preferences, and competitor analysis
- Social media data: Uncover customer sentiment, brand perception, and emerging trends in the market
- Government databases: Provide demographic information, economic indicators, and industry-specific statistics
2. Data Integration
After collecting the data, it is brought together from multiple, often disparate, sources and merged into a unified, cohesive dataset. This stage involves cleaning, transforming, and standardizing the data to ensure it can be analyzed together.
- Data Extraction: Extracting relevant data from various sources in their native formats
- Data Transformation: Transforming the extracted data into a consistent format suitable for analysis. This might include cleaning inconsistencies, handling missing values, and standardizing units
- Data Loading: Loading the transformed data into a central repository, such as a data warehouse or data lake

3. Data Management
Data is only valuable if it’s accurate, reliable, and secure. Data management encompasses several key aspects like cleaning, sorting, and safeguarding sensitive information.
- Data Quality: Maintaining data accuracy and completeness by identifying and resolving errors, inconsistencies, and missing values
- Data Governance: Establishing policies and procedures for data access, ownership, and usage to ensure responsible data utilization
- Data Security: Implementing safeguards to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss
Also Read- How Revenue Intelligence Boosts Your Sales Growth
4. Data Analysis
Using analytical techniques like statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling, BI tools identify trends, correlations, and anomalies in the data.
- Descriptive Analytics: Provides a summary of past performance, answering “what happened” questions. For instance, what were the sales figures for the previous quarter? How many website visitors did we have last month?
- Diagnostic Analytics: Dives deeper to identify the “why” behind trends and issues. Imagine asking questions like, why are sales declining in a specific region? What factors contribute to customer churn?
- Predictive Analytics: Leverages statistical models and machine learning to forecast future trends. This allows you to answer “what if” questions. Predict what the demand for your product will be next year or how a price change might affect revenue
- Prescriptive Analytics: Goes beyond just predictions. It recommends specific actions to optimize performance based on the analysis. Imagine getting insights like “adjusting marketing campaigns in region X can potentially boost sales by Y%.”
Also Read- Self-Service Business Intelligence: Everything You Need to know
5. Data Visualization
Data visualizations are the storytellers of BI. They take complex data and present it in a visually appealing and easily understandable format – dashboards, charts, graphs, or heatmaps.
- Charts and Graphs: Bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts effectively illustrate trends, comparisons, and relationships within the data
- Dashboards: Interactive dashboards provide a comprehensive overview of key metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis
- Maps: Geographical visualizations can reveal regional trends and patterns in customer behavior or sales performance
Case Study Video: Transforming Healthcare with Advanced Business Intelligence Solutions
Learn how Kanerika helped the business operations of a renowned medical technology company through the automation of workflows and responsive customers with Power BI.
Benefits of Business Intelligence
1. Accurate Reporting and Monitoring of KPIs
Business Intelligence tools allow businesses to quickly generate reports and monitor key performance indicators, improving efficiency and decision-making.
2. Improved Business Insights
It helps get valuable insights by analyzing data from various sources, enabling organizations to make more informed and strategic business decisions. By providing clear and concise data visualizations and analysis, BI allows leaders to make informed decisions based on concrete evidence.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making
With BI, organizations get accurate, up-to-date, and quality data which they can use for performing analysis quickly. Access to dashboards and reports helps managers spot trends and patterns, making it easier to plan business strategies effectively.
4. Increased Efficiency
BI automates data collection, analysis, and reporting processes, reducing manual effort. This saves time and improves productivity, allowing employees to focus on strategic tasks rather than routine data management.
5. Operational Optimization
Organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of improvement within their operations. For instance, supply chains can be optimized based on predictive models generated through BI.

6. Competitive Advantage
Gaining insights into market trends, competitor strategies, and customer behavior gives businesses a competitive edge. They can respond proactively to market shifts and capitalize on opportunities before their competitors.
7. Financial Management:
BI tools can analyze expenses, revenues, and profit margins to identify financial inefficiencies. They help detect wasteful spending and improve budgeting, ultimately driving higher profitability.
8. Risk Reduction
Business Intelligence offers predictive analysis that helps businesses anticipate and mitigate potential risks. For instance, companies can spot potential fraud, identify supply chain risks, or foresee market fluctuations.
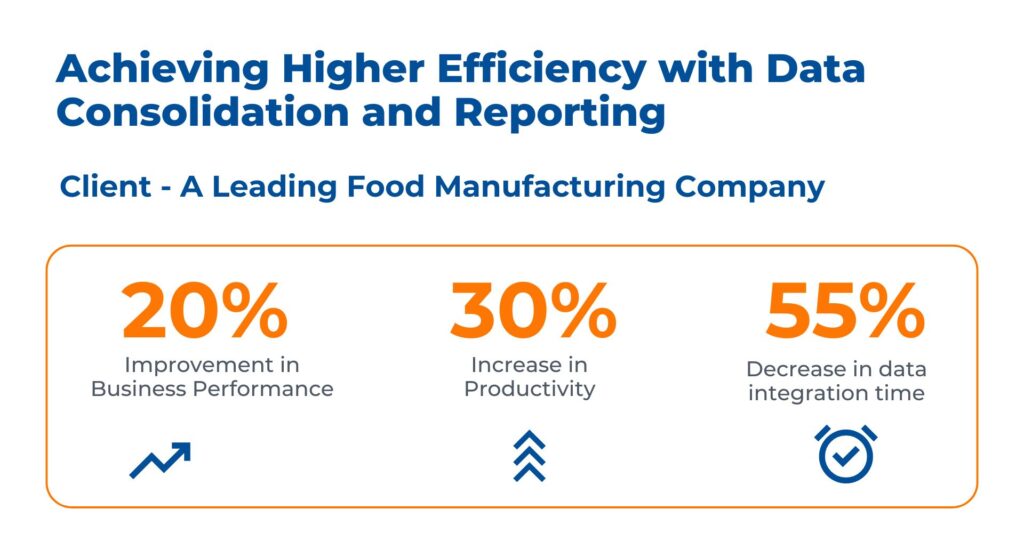
Case Study: Data Consolidation and Reporting Using Power BI
The client is an edible oil manufacturer and dealer who uses SAP systems for all major company transactions. They faced challenges with unstructured data, making real-time reporting on sales, deliveries, payments, and distribution a complex task. Inconsistent and delayed insights due to dispersed SAP and non-SAP data hindered accurate decision-making
Kanerika resolved its data management problems through the following:
Best Practices for Building a Winning Business Intelligence Strategy
1. Understand Objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Begin by identifying the goals that the BI strategy should support, such as boosting sales, improving customer satisfaction, or enhancing operational efficiency. From these goals, derive specific KPIs to measure success.
2. Assess Current Data Infrastructure
Analyze the existing data infrastructure to understand current capabilities and identify gaps. Determine the sources of data, quality, and how it’s managed. This will guide decisions on new tools or processes that need to be incorporated.
3. Identify Stakeholders and Involve Them:
Include key stakeholders from various departments (IT, finance, marketing, etc.) in the planning process. Their input will help tailor the BI strategy to the organization’s specific needs, ensuring better adoption later.
4. Choose the Right BI Tools
Evaluate different BI tools based on the organization’s data infrastructure, size, and goals. Consider factors like ease of use, integration with existing systems, scalability, and cost.
5. Establish a Data Governance Framework
Implement rules and protocols to ensure data quality, security, and privacy. Define roles and responsibilities for data management to ensure accuracy and compliance.

6. Create a Data Integration Plan
Develop a plan to aggregate data from different sources into a unified data warehouse. This step ensures that your BI tools can analyze a complete and consistent dataset.
7. Develop Data Models and Reports
Design data models that align with your KPIs, ensuring relevant data is available for analysis. Create reports and dashboards tailored to different users and departments.
8. Train Users and Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Conduct training sessions to help stakeholders understand and use BI tools effectively. Cultivate a culture that values data-driven decisions, encouraging employees to rely on insights generated.
9. Implement and Monitor the Strategy
Roll out the BI solution gradually to address potential issues early on. Monitor performance regularly and refine the strategy to adapt to evolving business needs.
10. Review and Update
Regularly review the strategy’s effectiveness, gathering feedback from users and adjusting tools, processes, and objectives to maintain alignment with business goals.

Top Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
Known for its powerful data visualization capabilities, Tableau offers an easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface. It integrates seamlessly with multiple data sources, enabling users to create interactive dashboards for comprehensive insights.
A cloud-based BI tool, Power BI provides robust data visualization and reporting features. Users can build and share reports with real-time data from various sources, and it integrates well with other Microsoft products.
Qlik Sense features associative data indexing to reveal hidden connections and trends. Its flexible self-service analytics enable users to build their own dashboards and apps.
A comprehensive suite offering data discovery, visualization, and reporting tools. SAP BusinessObjects integrates with SAP’s ERP software, providing in-depth insights for organizations already using SAP systems.]
Acquired by Google Cloud, Looker provides powerful data exploration and visualization. Its modeling layer makes it easy to define metrics and build custom dashboards.
Domo is a cloud-based platform known for its scalability and collaborative data dashboards. It connects with hundreds of data sources and provides tools to build apps that automate workflows.
IBM Cognos combines AI and machine learning to offer predictive insights, data visualization, and automated reporting. Its natural language querying makes data exploration accessible to non-technical users.
Sisense specializes in handling large data sets and offers both cloud and on-premises deployment. Its analytics capabilities provide actionable insights through intuitive dashboards.

Business Intelligence at Work: Applications Across Industries
2. Logistics and Supply Chain Management
BI systems can track every link of the supply chain in real-time, providing insights into inventory levels, demand forecasting, and vendor performance. This data can improve inventory management, reduce delays, and optimize distribution routes. Predictive analytics can also help identify potential bottlenecks and mitigate risks before they occur.
3. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use BI to monitor production lines, optimize machine efficiency, and reduce downtime. By analyzing historical production data, companies can identify trends and inefficiencies to streamline production schedules. Quality control data also ensures products meet regulatory standards.
4. Insurance
Insurance companies employ BI tools to assess risk, detect fraud, and improve customer profiling. By analyzing historical claims data, companies can predict future claim trends and adjust premiums accordingly. BI also helps insurance firms segment customers for tailored marketing.

5. BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance)
In the BFSI sector, BI systems help identify profitable customer segments, assess credit risks, and detect suspicious transactions to combat fraud. Dashboards can track key financial metrics in real-time, enabling quick adjustments to lending policies and investment strategies. BI also assists in ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
5. Retail
BI analyzes customer data, sales patterns, and inventory to optimize pricing strategies and personalize marketing campaigns. Retailers can use BI to track consumer preferences, improve product recommendations, and manage inventory levels. For example, analyzing past purchasing behavior helps stores identify high-demand products and avoid stockouts, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
6. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use BI to improve patient care, manage resources, and ensure compliance. Analyzing patient data enables hospitals to identify high-risk patients and reduce readmission rates. BI also helps track resource utilization to optimize staffing and minimize equipment downtime. Additionally, predictive analytics can identify disease outbreaks or forecast patient admission trends, helping facilities prepare effectively.

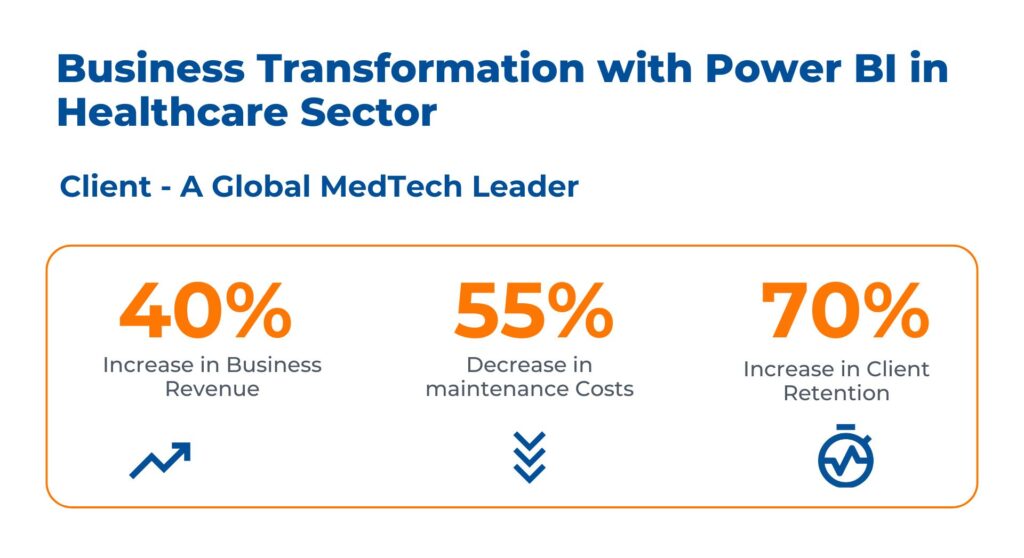
Case Study: Business Transformation with Power BI in Healthcare
The client is a prominent global HealthTech enterprise. They sought immediate access to a business intelligence dashboard to tackle challenges from aging populations, budget reductions, rising expenses, and apprehensions about patient safety within the medical device sector.
By utilizing the Immense capabilities of Power BI, Kanerika addresses these challenges by:
- Implementing comprehensive medical device lifecycle tracking and data architecture using MSFT Power BI use cases
- Transforming legacy data into a new platform for real-time analysis, resulting in improved business intelligence using Power BI templates for healthcare
- Deploying solution on Azure cloud, enabling scalable performance, data aggregation, and decision-making
Stay Ahead in Data Management with Kanerika’s Advanced BI Solutions
As a leader in data analytics and management, Kanerika is your go-to consulting partner for utilizing your business data efficiently. By leveraging a wide range of cutting-edge business intelligence tools and technologies, we empower organizations to transform their processes, boost productivity, enhance efficiency, and drive superior performance.
With a proven track record of successful BI project implementations across diverse industries, including healthcare, logistics, and finance, Kanerika has the expertise to tackle any data challenge hindering your business operations. Our team of seasoned BI consultants combines deep technical know-how with a keen understanding of industry-specific requirements to deliver tailored solutions that deliver tangible results.

Frequently Asked Questions
[faq-schema id=”14757″]
